DeFi, or decentralised finance, represents an innovation driving the digital transformation of financial services. The technology behind this innovation is based on secure distributed ledgers, like those used by cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Whether savings accounts, lending/borrowing facilities, asset management or even more complex products, these financial instruments are provided through a peer-to-peer framework without an intermediary such as a bank or broker. This has opened access to these products worldwide. The only requirements are an internet connection and a digital wallet (such as MetaMask) that can run on the blockchain, primarily Ethereum. There is a broad range of wallets available like Avalanche, Solana and Binance Smart Chain, to name a few.
These blockchains and the services they provide run on smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts written in code, with the terms of the agreement explicitly written and stored across the distributed network.
Trade finance represents the financial instruments and products companies use to facilitate international trade and commerce.
- Trade finance makes it easier for importers and exporters to transact trade business.
- Trade finance can help reduce the risk associated with global trade by reconciling the divergent needs of an exporter and importer.
- “Some 80 to 90 per cent of world trade relies on trade finance (trade credit and insurance/guarantees), mostly of a short-term nature.” — WTO
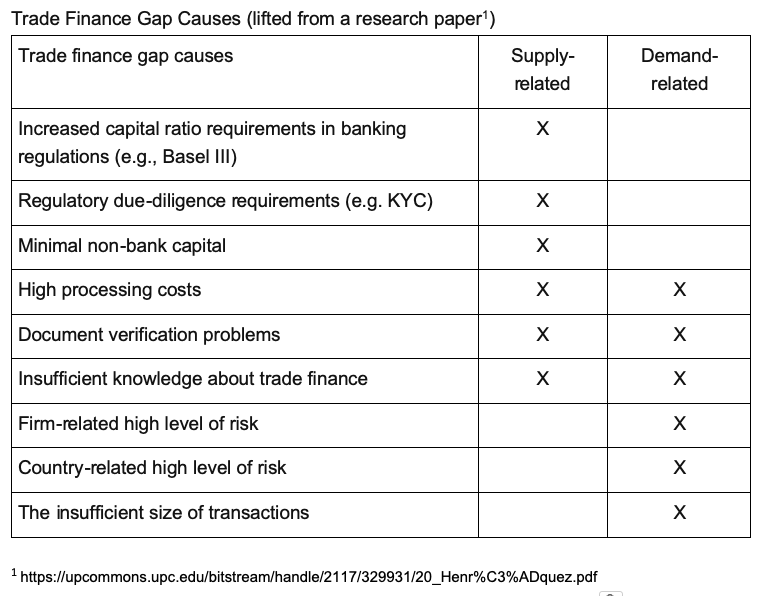
Trade finance provides the exporter with receivables or payments based on the agreement that the importer might be extended credit for the trade order. The persistent gap between supply and demand in the trade finance market has led to a lack of financing for SMEs, impacting global trade and creating inefficiencies and bottlenecks. One solution involves leveraging distributed ledger technology, particularly DeFi, to expand credit supply and digitise and standardise some of the processes involved in Trade Finance.